
The neutral zone trap—also known as the “trap”—is a defensive strategy in hockey, designed to apply extensive pressure to an opposing offense as they try to take the puck through the neutral zone. Loading up the neutral zone with defenders severely inhibits the ability of an offense to get the puck up the ice.
Also, how do you use the neutral zone trap?
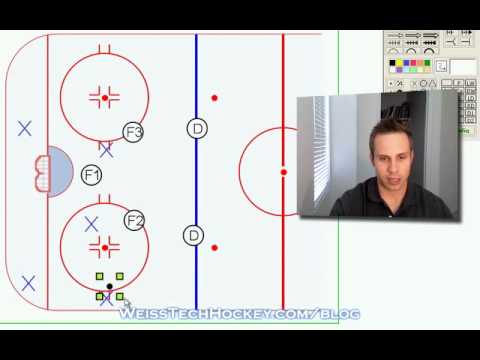
Similarly, is neutral zone trap banned? But in 2020 teams in the NHL are still using the neutral zone trap to protect leads and win hockey games. While the concept is the same, the execution of the neutral zone trap has changed ever so slightly. However, like most teams, they have realized this type of defensive system wins.
Beside the above, what is the neutral zone and how is it used? In gridiron football, the neutral zone is an area in which no member of either team may be, other than the person holding the ball. The neutral zone only exists in dead ball situations (i.e. when play is not ongoing).
Amazingly, what is the purpose of the neutral zone in hockey? Why is the neutral zone in hockey important? The neutral zone is important because it dictates the pace of the game. Teams must figure out how to skate into the opposing team’s zone if they want to increase their shot totals and, consequently, goal totals.It starts every game, period and play. The faceoff is used to begin every game, period and play. It occurs when a referee drops the puck between the sticks of two opposing players.
What is the dead puck era?
Dead puck era. Following the 1994–95 lockout, the NHL entered a prolonged period of offensive decline. Throughout the 1980s, 7.6 goals were scored per game on average. That figure had dropped below six goals per game by the 1994–95 season, and to 5.19 by 1998–99.
Who invented the trap NHL?
Who invented the trap in hockey? It is unclear who invented the trap in the National Hockey League, but Jacques Lemair is credited with popularizing the system during the 1990s. Lemair led the New Jersey Devils with the system during a game against the Detroit Red Wings in the 1995 Stanley Cup Finals.
What is a neutral zone infraction?
It is a Neutral Zone Infraction when: a defender moves beyond the neutral zone prior to the snap and is parallel to or beyond an offensive lineman, with an unimpeded path to the quarterback or kicker, even though no contact is made by a blocker; officials are to blow their whistles immediately.
Is there positions in hockey?
There are six positions in hockey: three forwards—comprised of a centre and two wingers—two defencemen, plus one goaltender. … The centre is flanked on the right and left by wingers, who generally play along the boards on their respective sides of the ice.
What’s the difference between neutral zone infraction and offsides?
How do I distinguish between offsides, neutral zone infractions, and encroachment? … Offsides – Lining up over the line of scrimmage, past the football. Neutral Zone Infraction – Similar to offsides, but happens on the interior defensive line, with a clear path to the quarterback or the kicker.
What’s the difference between neutral zone infraction and false start?
Neutral zone infraction (5 yards) – A neutral zone infraction is when a defensive player crosses the line of scrimmage prior to the snap and then causes an offensive player to move. Rather than call a false start on the offense, the penalty is called on the defensive player.
What is the trap defense in hockey?
The neutral zone trap (often referred to as simply the trap) is a defensive strategy used in ice hockey to prevent an opposing team from proceeding through the neutral zone (the area between the blue lines) and to force turnovers.
How do you beat trap defense in hockey?

How many periods are there in hockey?
The time allowed for a game shall be three (3) twenty-minute periods of actual play with a rest intermission between periods.
What is the left wing lock in hockey?
The left wing lock is a defensive ice hockey strategy similar to the neutral zone trap. In the most basic form, once puck possession changes, the left wing moves back in line with the defencemen. Each defender (including the left winger) plays a zone defence and is responsible for a third of the ice each.












